Development of the lab- and semi-industrial scale technologies for cannabidiol isolation
Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa) is one of the oldest annual crops which is known to contain more than five hundred compounds, of which more than one hundred are Phyto cannabinoids. The two major cannabinoids (and those best known for their therapeutic potential) are Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), i.e., the neutral homologues of THCA and CBDA, respectively (Fig. 1). Δ9-THC is a well-known natural psychotropic compound, which is accumulated in industrial hemp in minimal amounts – 0.2% w/v– approximately 50 times less than that found in marijuana, and therefore Cannabis sativa is only allowed for cultivation in European countries.
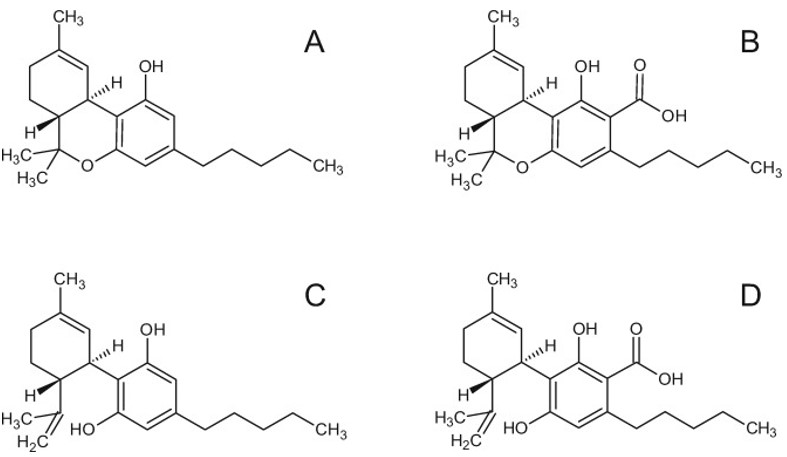
Structures of THC (A), THCA (B), CBD (C), and CBDA (D).
Non-psychotropic CBD and its parent compound CBDA were reported in various C. sativa cultivars as the major quantitatively cannabinoids [5].
Recently, there has been a dramatic increase in CBD-rich supplementation in the food supplement and cosmetic industries. Even more potential is reported on the pharmaceutical use of cannabinoids. CBD has been given considerable attention due to its plethora of therapeutic properties and pharmacological activities such as analgesic, antibacterial, antidiabetic, antiemetic, antiepileptic, anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative, antipsychotic, antispasmodic, etc. Therefore, cannabinoids are considered as promising natural compounds in treating epilepsy, pain, depression, anorexia, cancer and other diseases. Moreover, processing of industrial hemp generates vast amounts of by-products containing substantial amounts of important compounds, such as other nonintoxicating Phyto cannabinoids, terpenes, and phenolic compounds with potential pharmaceutical values as drugs or supplements.
Growing adoption of CBD-infused products in industries such as pharmaceuticals, personal care, cosmetics, and nutraceuticals, along with medical applications, CBD is seeing monumental demand in Europe and according to Grand View Research report, the European market is on course to grow 400% over the next four years.
There are no standard solutions for CBD production from hemp biomass, however, the entire extraction/distillation process usually follows these basic steps: extraction, winterization, decarboxylation, vacuum distillation, crystallization, and/or purification of CBD by flash chromatography. In order to fully exploit the pharmacological potential of CBD it will be essential to have highly pure cannabidiol preparations, especially without the psychoactive contaminants such as THC. Such preparations must be obtained using methods that are easy, relatively inexpensive, and capable of scale-up.
This project is being carried out in collaboration with Hemptec OÜ, who wish to set up a CBD production plant in Estonia.

Super critical CO2 extractor

CBD products
-
- Cold ethanol extraction (-40C)
- Supercritical CO2 extraction
- Molecular distillation
- Crystallization
- Purification by flash chromatography

Ethanol extractor



